The GMAT exam is a test used by most of the graduate business degree as a selective tool for future students. It is meant to evaluate your commitment to and eligibility for the MBA or business master’s degree. The test evaluates your problem-solving and critical reasoning skills. A strong GMAT score dramatically improves your chances of getting into a university. In a Kaplan/Manhattan Prep survey, 88% of business schools said that submitting a competitive admissions exam score will help your application. It is a challenging test that lasts for around 2 hours and must be studied in advance.
I started studying for the GMAT during the summer of 2023 and didn’t expect it to be this challenging. On my first prep test, I got a 570, far from the 700+ I needed to get into my dream school. After several months of trial and error, I finally got a 720 (old GMAT version, equivalent to a 655 on the Focus Edition)! Knowing how the score works helped me a lot. A key tactic is to improve in what you are bad at and not improve your strengths!
If you have already researched the GMAT, you might have encountered two different GMAT exams: the Focus GMAT and the old GMAT. They have been updated recently, making the new exam version shorter. So be careful not to get mixed up when you read about it.
How is GMAT Calculated, and How Can You Take this to Your Advantage?
Contents
The Three Section
Overall Score Calculation
How to Crack the GMAT
Resources
The Three Sections
The Quantitative section evaluates your capacity to reason quantitatively, solve quantitative problems, and interpret graphic data. It consists of 21 multiple-choice problem-solving questions to be completed in 45 minutes. It measures algebraic and arithmetic foundational knowledge and your capacity to apply this knowledge to solve problems.
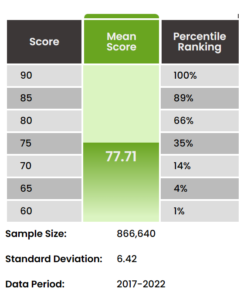
Quantitative Reasoning scores range from 60 – 90. The score is based on three factors: 1) the number of questions answered, 2) whether the answers are correct or incorrect, and 3) the difficulty and other parameters of the questions answered. The average score is 77.71, as shown in the graphics.
The Verbal Reasoning section consists of 23 multiple-choice reading comprehension and critical reasoning questions to be completed in 45 minutes. It measures your ability to read and comprehend written material and evaluate arguments. Reading Comprehension questions measure the ability to understand words and statements, understand logical relationships between significant points, draw inferences, and follow the development of quantitative concepts. Critical Reasoning questions measure the ability to make arguments, evaluate arguments, and formulate or evaluate a plan of action.
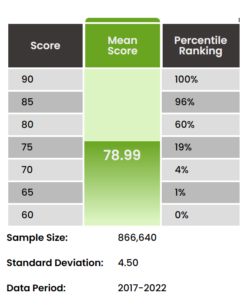
Verbal Reasoning scores range from 60 – 90, and the average score is 78.99.
Data Insights consists of 20 multiple-choice questions, to be completed in 45 minutes. The question types are data sufficiency, multi-source reasoning, table analysis, and graphics interpretation. It measures your ability to analyze and interpret data and apply it to real-world business scenarios. The Data Insights section of this exam leverages its question types to measure a newly calibrated digital and data literacy dimension—one of the most relevant and in-demand skills in business today.
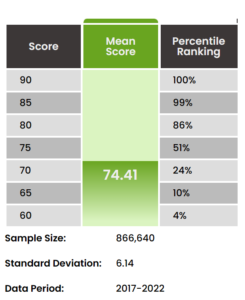
Data Insights scores range from 60 – 90. Some questions may have multiple parts.
Overall Score Calculation
The GMAT Focus score goes from 205 to 805. The important information about your score is not your final score but your percentile rank. The higher your score, the better your percentile rank. Your performance during the exam is compared with the other test takers from the past three years. Your percentile shows the percentage of test takers from the last three years with lower scores than yours. For example, if you are in the 76th percentile, you have scored better than 76% of people.
Look on your school website to know which percentile brackets you should aim for. In the GMAT, the extreme scores are extremely rare, so barely anyone gets even close to 205 or 805. Fewer than 50 out of 250,000 get a perfect score, meaning 805.
The GMAT assesses your score through the exam by computer calculations. Each time you get a question right, your score improves, and the next question you get will be more challenging. If you get that next (harder) question wrong, your score lowers, and your next question will be easier. After a few questions, the computer will know the level of questions you get wrong and, therefore, your level and score rank.
How to Crack the GMAT
So, what matters is not the number of questions you get correctly but the difficulty level of the question (and the percentage of people who got it right). The computer calculates the level of difficulty you missed, not how many answers you got correct. Those calculations mean for you that when you are studying, you need to focus on weak spots. You need never to get an easy question wrong, but you don’t always have to get a hard question right. When studying the GMAT, start with the easy questions, even if it seems counterintuitive. Master the easy and medium questions, which could lower your score immensely.
Each of the three sections (Quantitative, Verbal, and Data Insights) counts in your final score, and you need to score well in each. Study all three sections, even if you prefer the quantitative section, which seems to be the section most related to business school. A terrible score in one of the three sections will significantly drop your overall score. There is also a limit on how high your score can get with studying only two of the three sections.
However, during the exam, do not try to guess each question’s difficulty level. Most of the time, test takers are terrible at evaluating a question’s difficulty level. Also, getting an easier question does not always mean you got the last question wrong; for example, if you got all the questions right in a specific subsection -arithmetics, number properties, geometry- the test won’t have any hard questions to give you and will have to give you an easier question.
Remember that the GMAT is mainly about time management. Train yourself to answer the questions under pressure with limited time. Answering multiple questions badly in a row due to lack of time is deadlier than the same number of wrong answers spread in different parts of the tests. If you get five consecutive questions wrong, the level of the questions will go from hard to medium to easy, and you will end up with a low score. If it is spread out, you will have time to return to your past score in a few questions. Learn to finish the test on time!
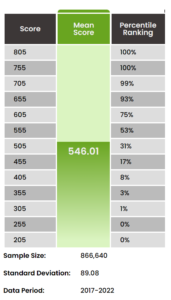
Here is the table of percentile ranking associated with a score.
Resources
The GMAT™ Focus Edition Scores (gmac.com) is the official GMAT site with all the exam details. They explain the material allowed on exam day, all the steps to take the exam, and more.
GMAT Club is a forum for everyone who is studying the GMAT. Students and experts write their questions and exam tips, which makes it a great resource. They talk about time management, stress, general concept explication, etc.
Consider getting a tutor if you have difficulty studying and improving your score. I have written an article on the subject, ranking the best ones (Best GMAT Tutors 2024). They really help me understand the concepts.
Remember that the GMAT score does not completely define your entrance to school. It is a test that needs to be studied and takes time. If you are running out of time, think about applying in the next round or year. Applying with a strong profile with a good GMAT score is better. There are many resources online that really help. One of the main challenges is having to study alone; those resources can provide you with the right support. Consider investing money in an online tutor if you are too far from your score goal.
